Shellfish, oily fish and white fish

Shellfish
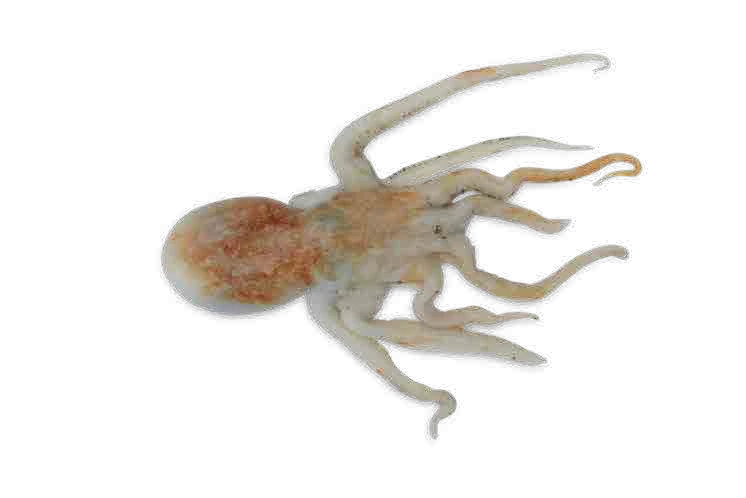
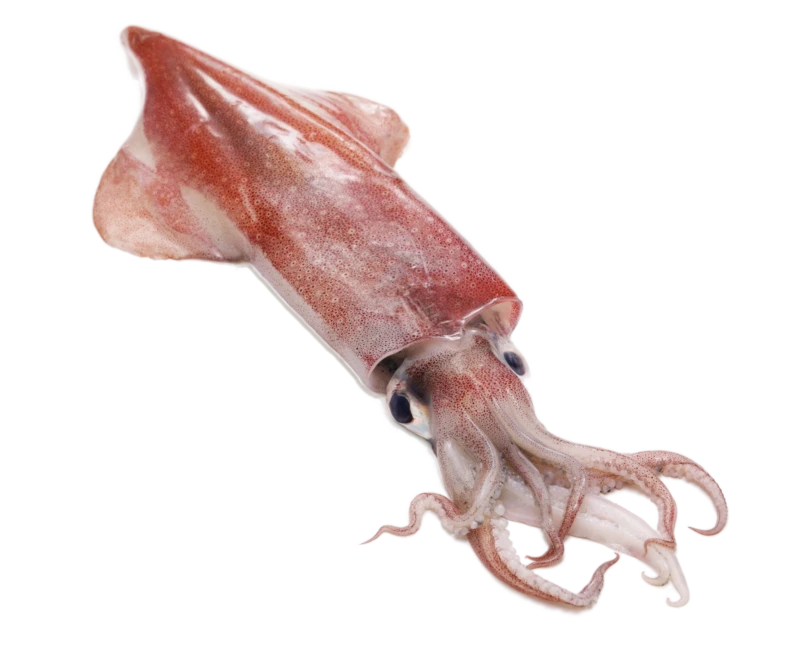
Molluscs
Molluscs are invertebrate animals with a soft body and a shell. They form part of an extensive and diverse group in terms of sizes, structural anatomy, behaviour and habitat, being classified into the following categories:
- Bivalves with two shells
- Univalves with one shell
- Cephalopods without a shell
Cephalopods belong to the largest and most evolved group of molluscs. The most common ones are octopus, cuttlefish and squid.






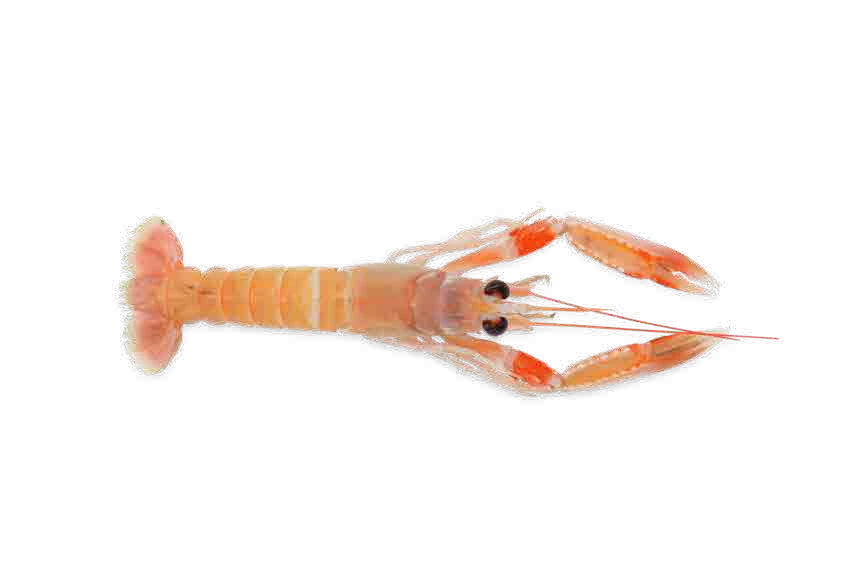
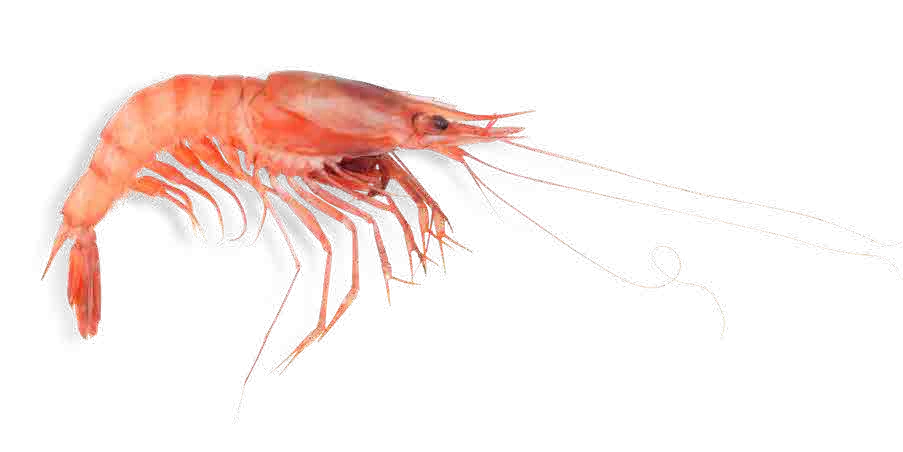
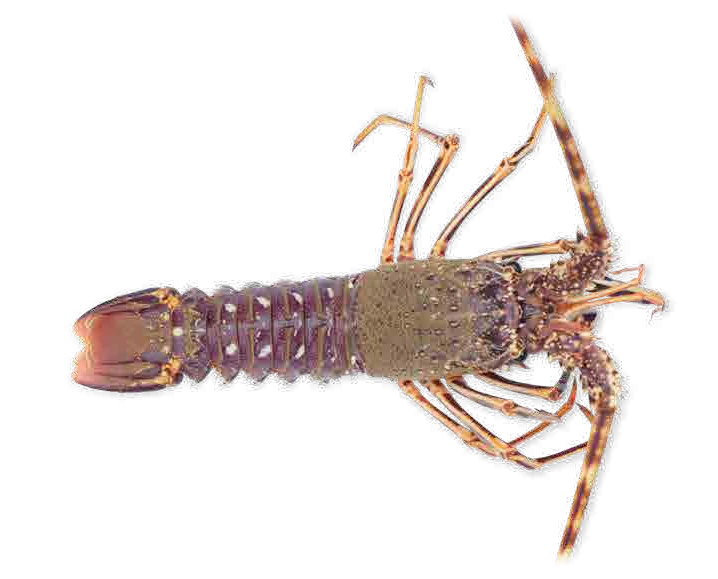
Crustaceans
Crustaceans are mostly aquatic animals that feed on small marine animals.
The body of a crustacean is divided into two parts: the head and thorax forming a unit (cephalothorax), and the abdomen. They have a pair of antennas, breathe through gills and are protected by a shell.


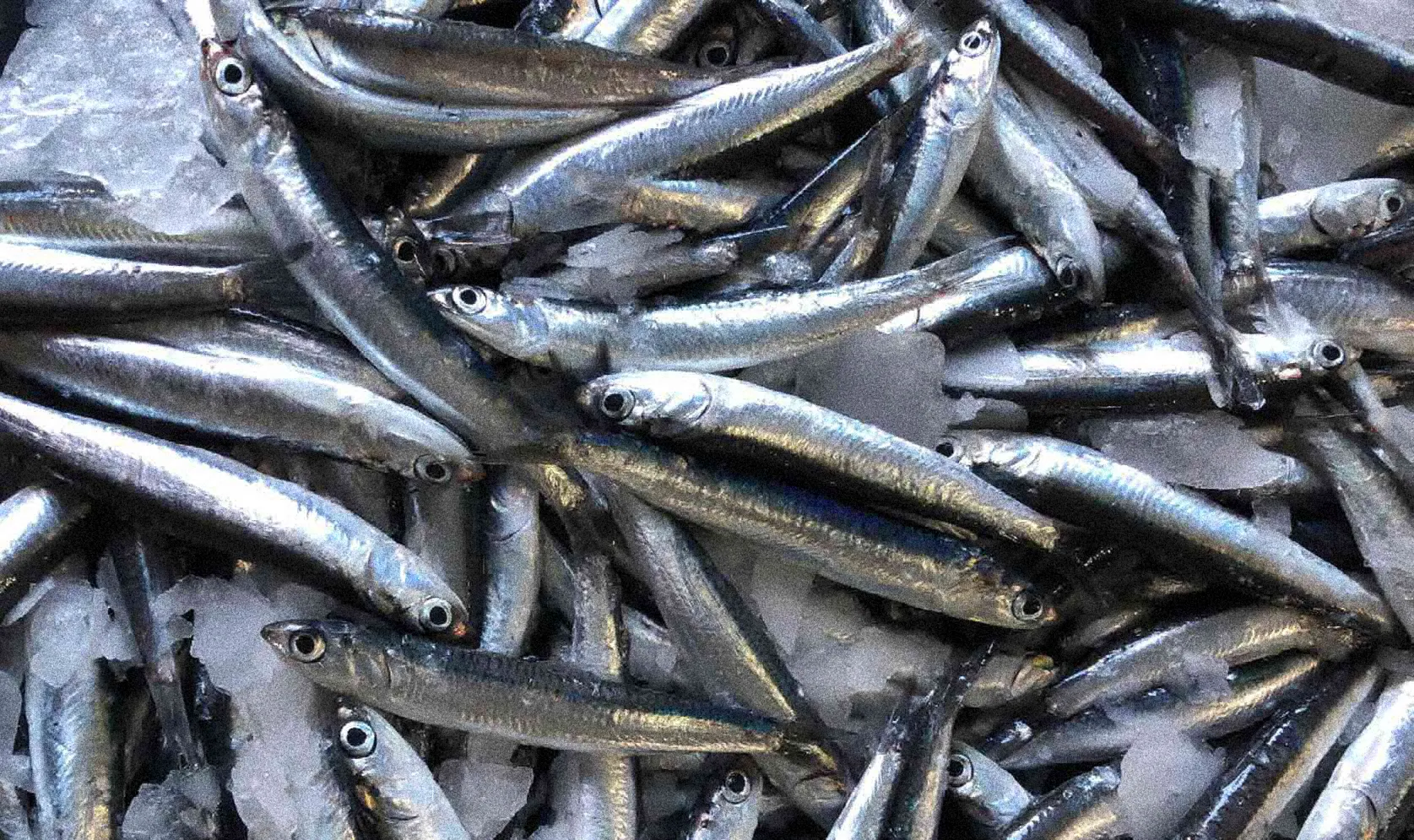
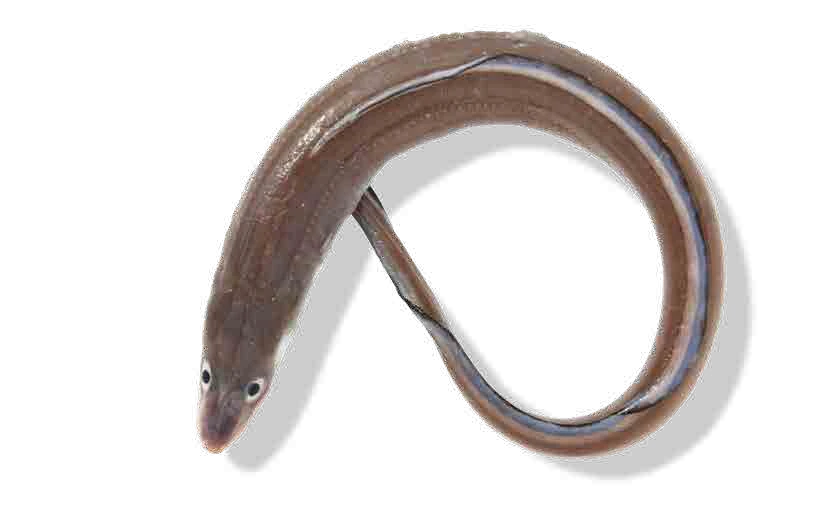
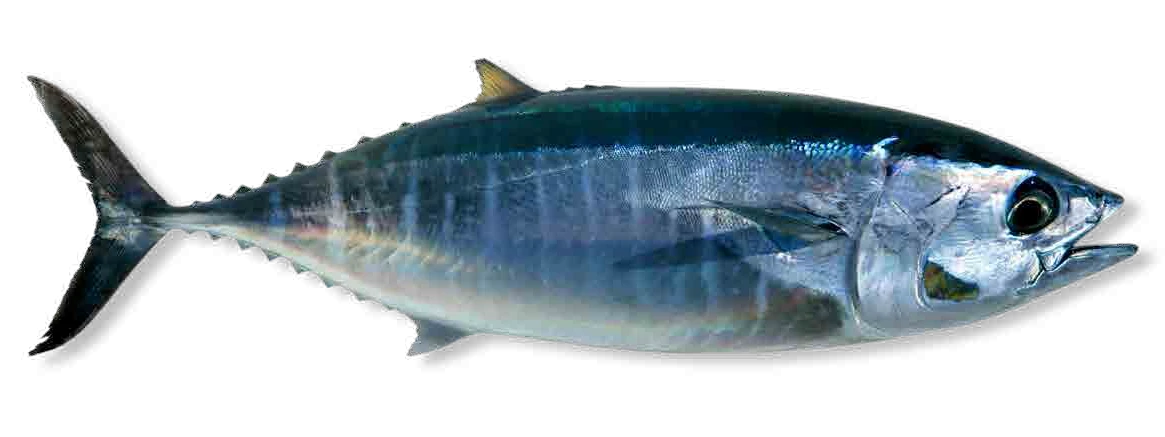
Bluefish owes its color to the amount of fat it contains, between 8 and 15% fat.
Oily fish
The main characteristic of oily fish is the proportion of fat they contain: between 8% and 15% in total.
The amount of fat influences their colouring and many oily fish have a blueish skin. This co- louring makes them invisible to predators, as they blend in with the blue of the sea viewed from above.
They are migratory fish that swim near the surface or between two bodies of water.
Oily fish have a high fat content, specifically Omega 3, which is very beneficial for preventing cardiovascular diseases. They are also a source of protein, vitamins and minerals.







White fish is a type of fish with low fat content in the muscle, between 0.4% and 5%.
White fish
White fish is a type of fish with low fat content in the muscle, between approximately 0.4% and 5%.
The term “white” is used because the majority of fish have lighter meat, as fat has an influence on their colouring. White fish have less fat because they usually live on the seabed and do not swim a lot.
0,4% - 5%
Fat
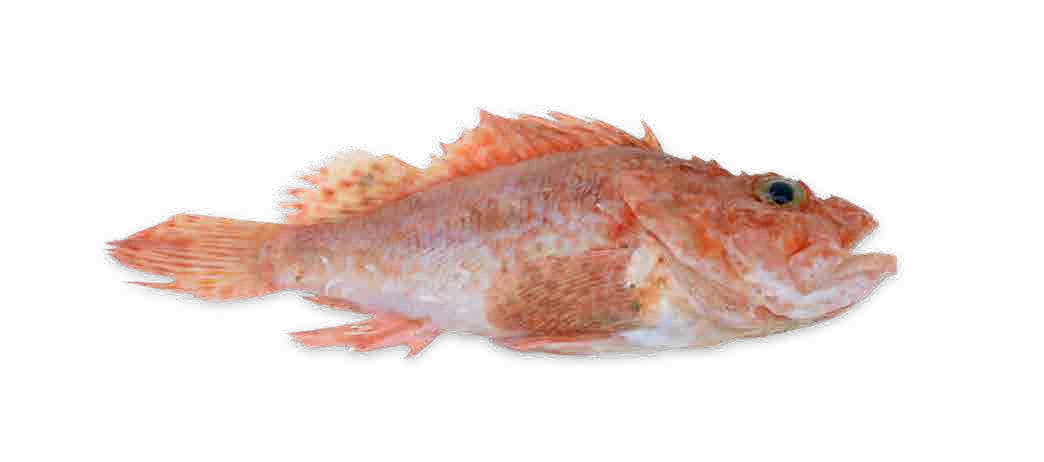






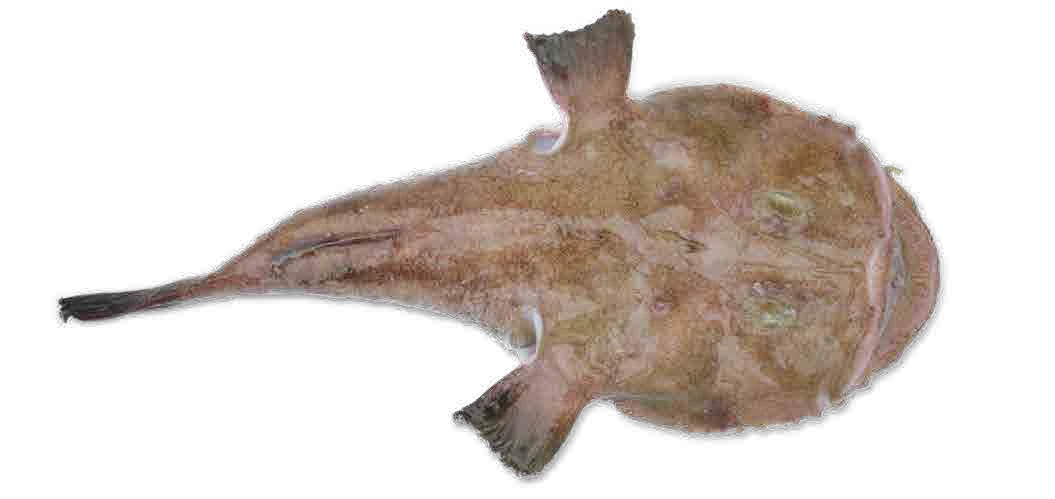
Interesting shapes
Monkfish
They have a branch-like extension over their eyes, with a small pouch full of luminescent bacteria. The light generated lures in their prey.

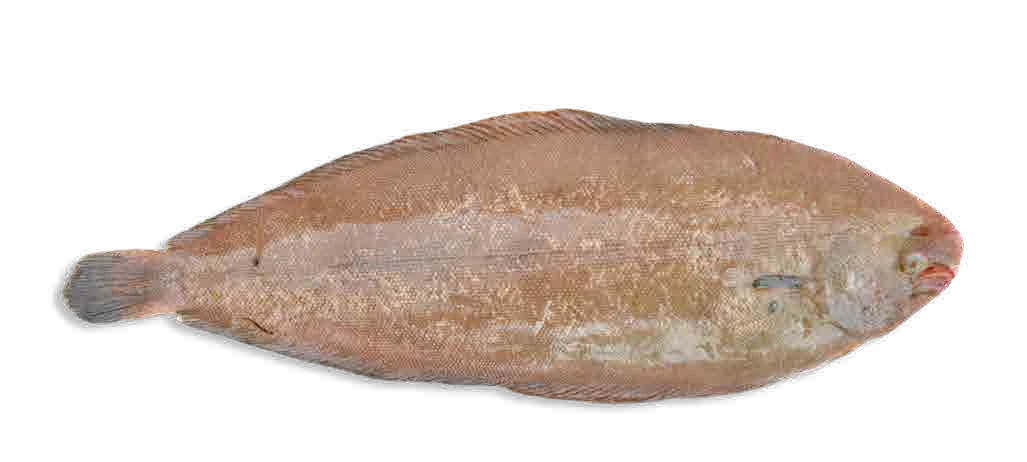
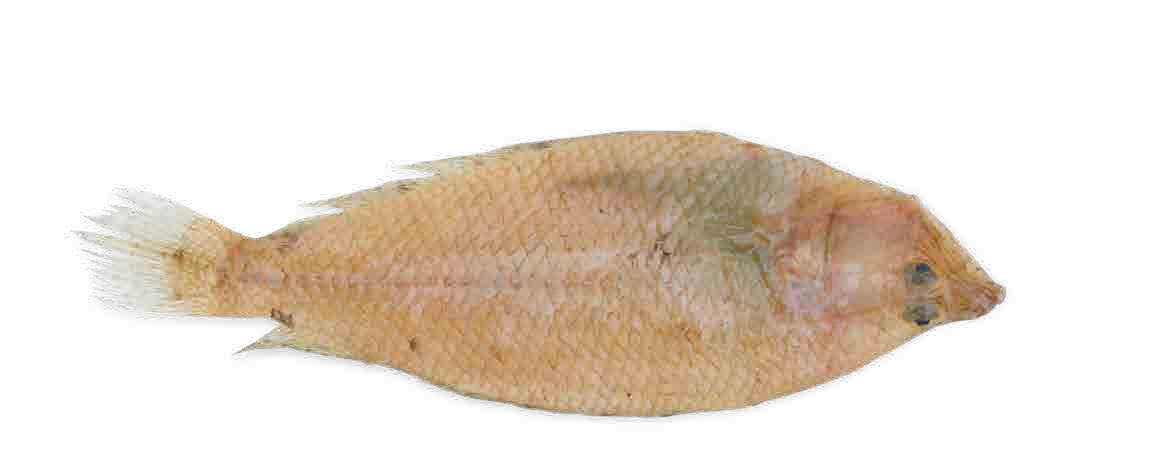
Flatfish:
sole, flounder and turbot
Oval and flattened body with both eyes close together and located on the right of the head. They swim on their left-hand side. At birth, they have the same shape as a white fish, but during growth their left eye begins to migrate towards the right-hand side.


 English
English  Català
Català  Castellano
Castellano  Français
Français